Safe.Privacy
Keeper
Market background
Market Background and Trends
Recent data breaches have led to a surge in financial fraud, account theft, and other cybercrimes, with
the scale of damages
continuously expanding. In this era, both businesses and individuals must take proactive measures to
strengthen security.



| Category | ‘20.8 ~12 |
‘21 | ‘22 | ‘23 | ‘24.1 ~8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
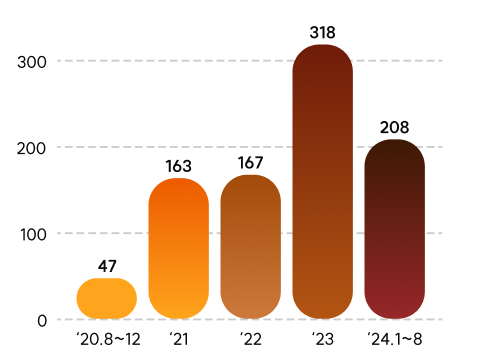
| Total | 47 | 163 | 167 | 318 | 208 |
| Public Institutions |
5 | 22 | 23 | 41 | 74 |
| Private Companies |
42 | 141 | 144 | 277 | 134 |
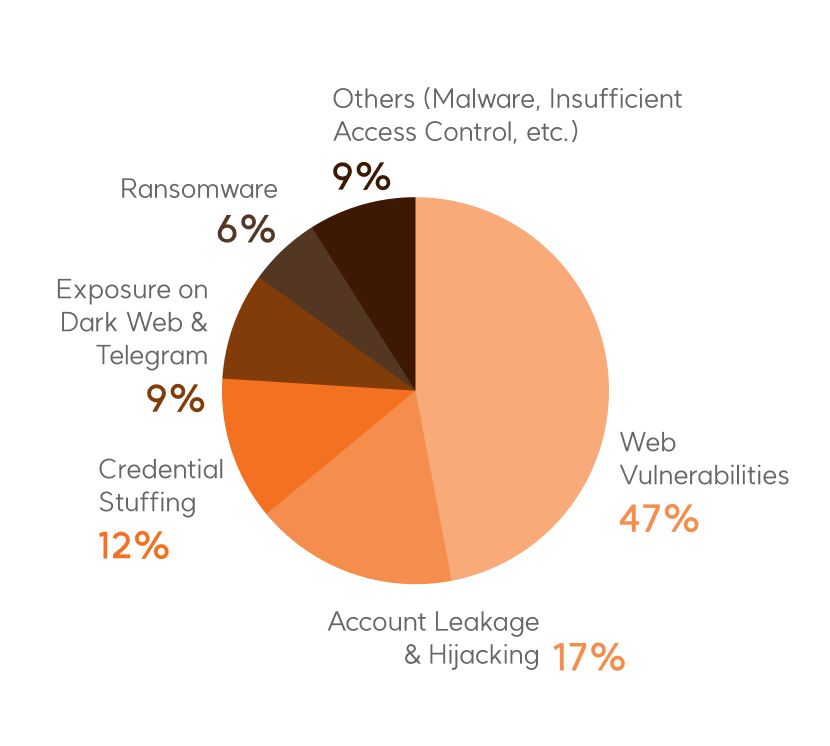
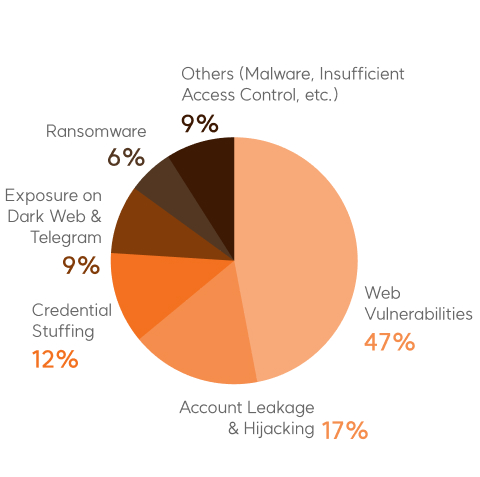
System Error (12%)
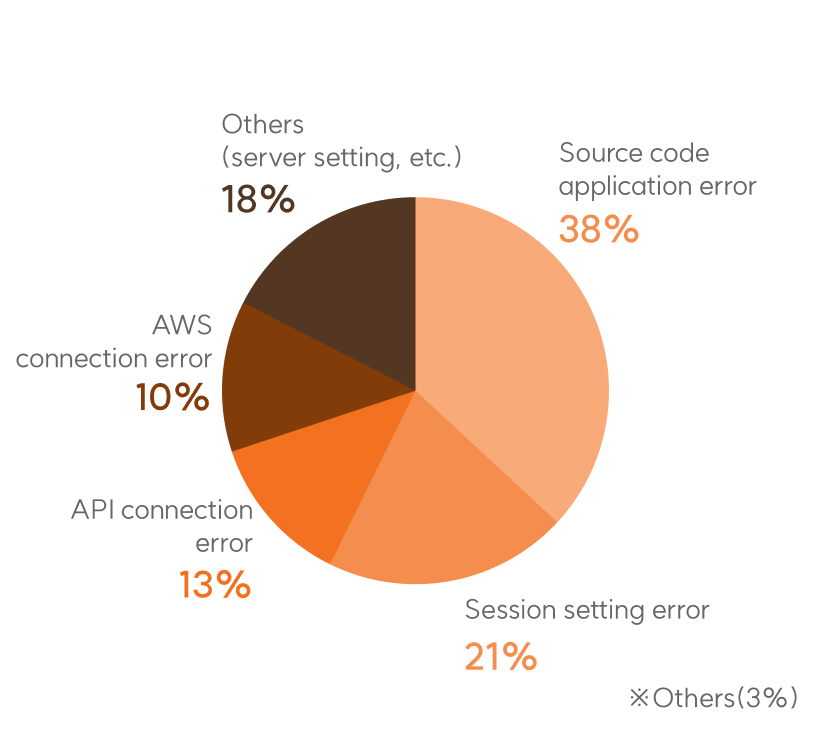
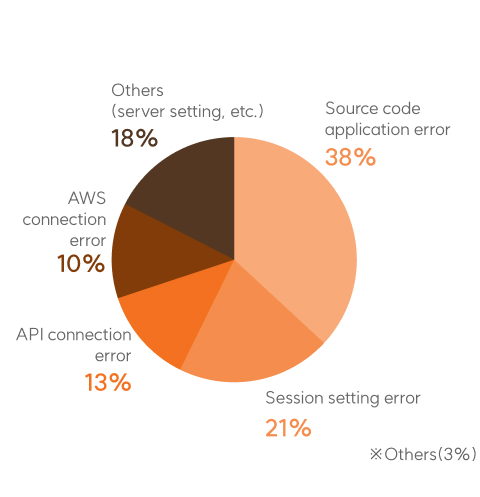
- While the number of reported personal information breaches in 2020 (August to December) was 47, it has steadily increased to △163 cases in 2021, △167 cases in 2022, and △318 cases in 2023.
- Among these, the number of cases in public institutions increased from △5 in 2020 to △41 in 2023. Private companies also showed an increasing trend, with the number rising from △42 in 2020 to △277 in 2023.
- In the period from January to August 2024, there were 208 reported personal information breach incidents, and 74 cases, corresponding to 35.6%, occurred in public institutions.
Personal Data Breaches
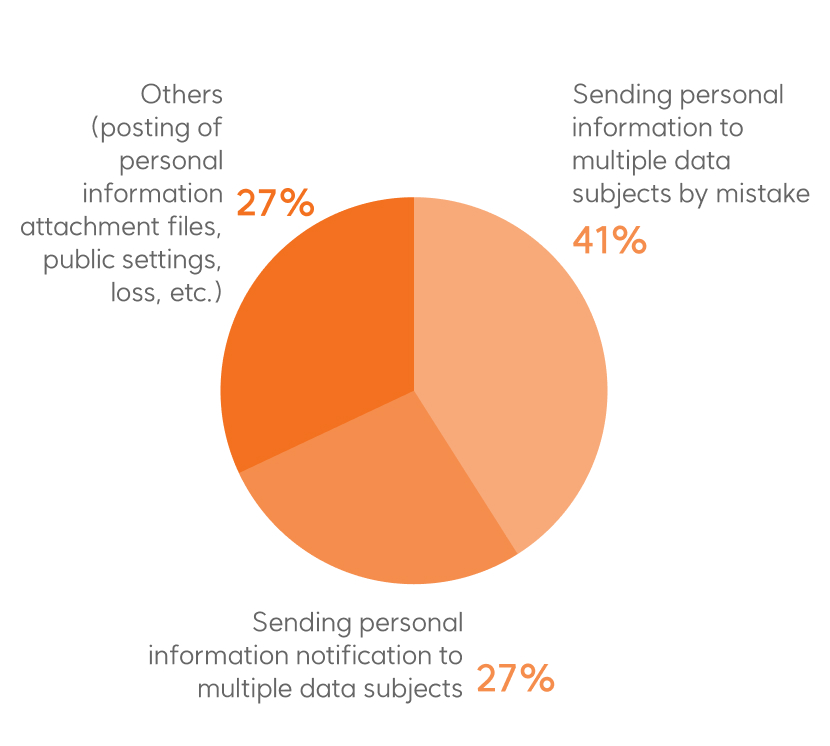
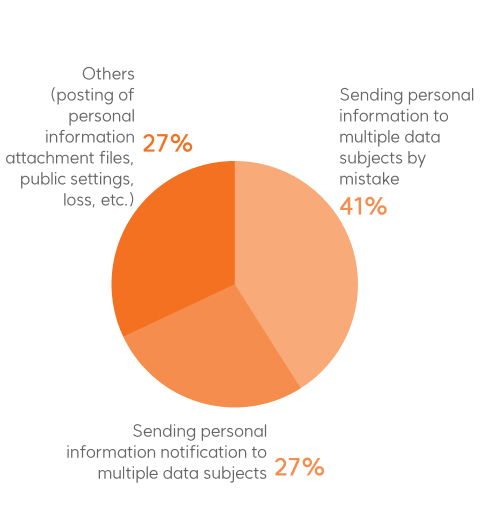
Personal data breaches occur due to both internal and external factors. Internally, causes include
employee negligence,
poor access control, and insider leaks, while external threats such as hacking, phishing, and malware
attacks pose significant risks.
These incidents can lead to severe consequences, including loss of trust, financial damages, and legal
penalties.


-
Internal Factors
- Negligence in handling personal information
- Work email - Leakage through attachments
- Employee error (mistake)
- Management negligence
-
External Factors
- Leakage due to external work
- Public service security negligence
- Hacking
-
Other Factors
- Leakage for work convenience
- Negligence in personal information management
can lead to loss of trust,
legal liabilities, and financial losses.
-
Financial Loss

Voice phishing and financial fraud using leaked personal information
-
Decline in Corporate Trust

Increased customer complaints and damage to brand image
-
Legal Issues

Increase in fines and lawsuits
-
Misuse of Personal Information

Spam emails, fraudulent calls, creation of fake accounts
with the Personal Information
Protection Act


- Article 21 of the Personal Information Protection Act (Compliance with the Criteria for Destruction of Personal Information)
-
Article 29 of the Personal Information Protection Act
(Duty to Take Safety Measures: Technical, Administrative,
and Physical Measures Applied)
- Article 23-2 of the Information and Communication Network Act (Restrictions on the Use of Resident Registration Numbers)
- Article 28 of the Information and Communication Network Act (Personal Information Protection Measures)
-
Personal Information Protection Act
-
1. Separate storage management measures when destroying and preserving personal
information
Article 21 (Destruction of Personal Information): The personal information controller shall destroy the personal information without delay when the retention period of the personal information has elapsed or the purpose of processing has been achieved.
Article 29 (Duty to Take Safety Measures): The personal information controller shall implement technical, administrative and physical measures to ensure the safety of personal information. -
2. Measures necessary for securing the safety of unique identification information,
etc
Article 24-2 (Restrictions on Processing of Unique Identification Information): The personal information controller cannot process unique identification information such as resident registration numbers, except as specifically permitted by law.
-
3. Duty of safety measures: technical, administrative and physical measures
Article 29 (Duty to Take Safety Measures): The personal information controller shall take technical, administrative, and physical measures to ensure the safety of personal information.
-
4. Criteria for imposing fines
Article 39-9 (Imposition of Fines, Etc.): Where a personal information controller leaks or misuses personal information in violation of the Act, he/she is subject to a fine of 3% of the maximum sales or not more than KRW 2 billion.
-
1. Separate storage management measures when destroying and preserving personal
information
-
Act on Promotion of Information and
Communication Network Utilization and Information Protection, etc-
1. Restriction on Use of Resident Registration Number
Article 23-2 (Restrictions on the Use of Resident Registration Number): Information and communication service providers may not collect and use resident registration numbers unless specifically permitted by law.
-
2. Technical, administrative and physical measures
Article 28 (Protection Measures for Personal Information): Information and communication service providers must take technical, administrative and physical measures to ensure the safety of personal information.
-
1. Restriction on Use of Resident Registration Number


 TOP
TOP





